For years I have been asked what the best medicine is for healthy aging, and my answer has always been the same. Exercise. A new study published in Cell by researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Xuanwu Hospital at Capital Medical University now helps explain why exercise is so effective. Even more interesting, it identifies a natural compound your kidneys already make, called betaine or Trimethylglycine, that can reproduce many of the same anti-aging benefits that come from consistent physical activity.
This research explains how exercise rejuvenates the body at the cellular level, and it validates clinical practices that have used betaine for years. These include protocols used in regenerative medicine clinics such as PUR-FORM.
The Exercise Paradox: Why One Workout Is Not Enough
Over six years, researchers conducted one of the most detailed studies ever performed on how the human body responds to exercise. Thirteen healthy young men were observed during three phases:
• A rest period after forty five days of inactivity
• A single workout
• Consistent running every couple of days for twenty five days
The findings were surprising. A single workout caused what the researchers called metabolic chaos. Stress hormone levels increased, amino acids were depleted, and inflammation rose. This is similar to the soreness and swelling many people feel after an unfamiliar or intense workout.
But when exercise became consistent, the body adapted in remarkable ways. Regular training reshaped the gut microbiome, strengthened the body’s internal antioxidant systems, and even reversed aging related changes in immune cells. These changes increased the number of “younger” immune cells while reducing the signals that accelerate aging.
Your Kidneys: The Hidden Control Center
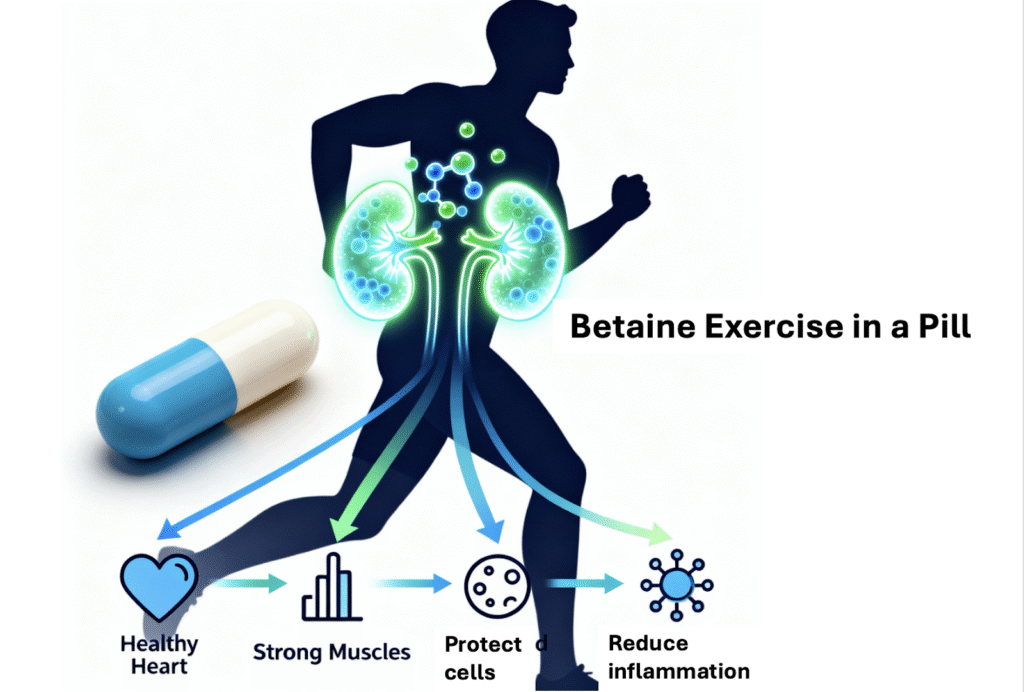
The most important discovery is that the kidneys act as a central control hub for the anti aging effects of exercise. During regular exercise, the kidneys greatly increase their production of betaine. This kidney produced betaine then sends youth preserving signals throughout the body.
Betaine binds to a protein called TBK1. TBK1 acts like a master switch for inflammation. By blocking TBK1, betaine prevents chronic low grade inflammation, which is one of the major drivers of aging. This explains why one workout is stressful, while consistent workouts are rejuvenating. Regular exercise allows the kidney betaine system to activate and restore balance.
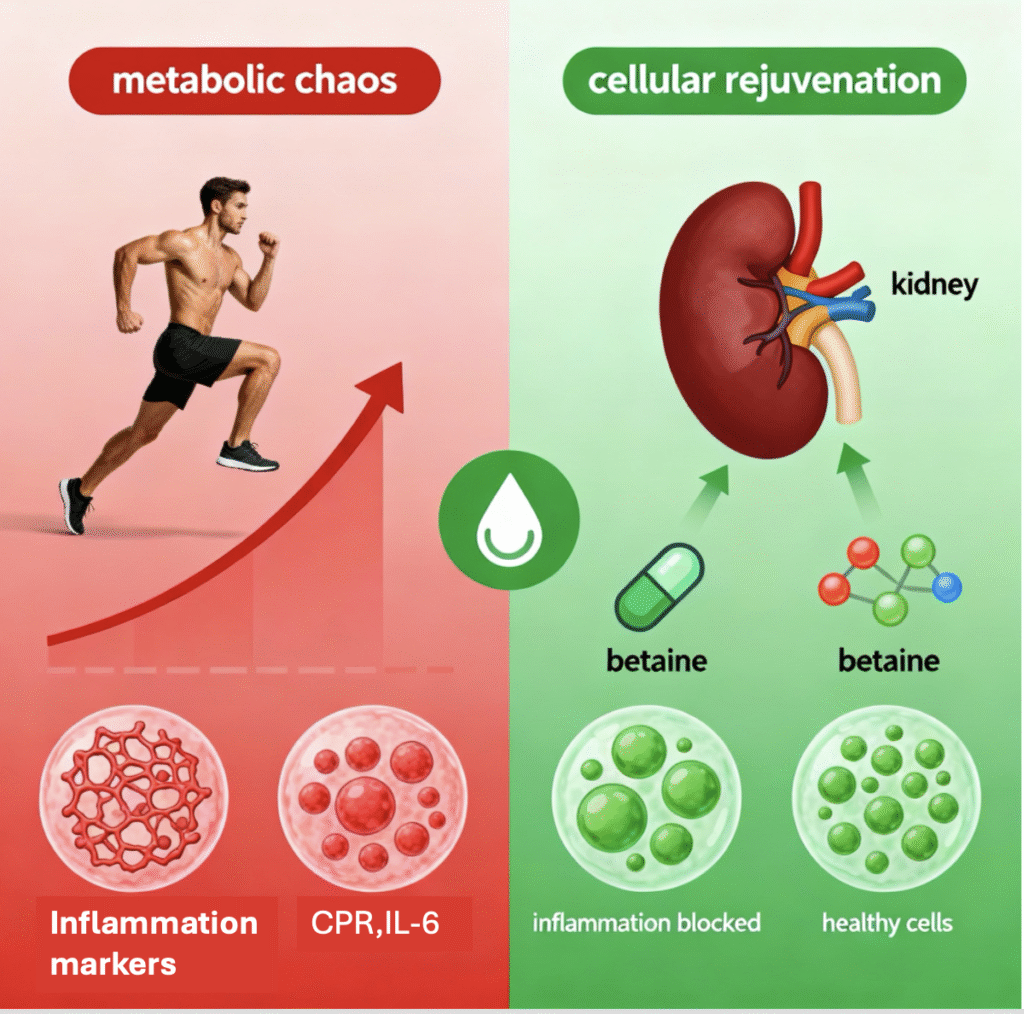
Can Betaine Replace Exercise
The research team then explored whether taking betaine as an oral supplement could mimic the effects of exercise. They gave aged mice betaine in their drinking water for eight weeks. The results were striking. Betaine levels in their kidneys rose to levels seen in regular exercisers.
These older mice experienced:
• Better balance and coordination
• Stronger muscles
• Improved memory and learning
• Fewer signs of depression
• Reduced fat accumulation and scarring in organs
• Healthier kidneys, liver, lungs, muscles, and skin
At the cellular level, betaine reduced markers of aging, supported healthier metabolism, improved kidney function, and decreased inflammation. It also activated longevity related pathways that help the body repair itself more efficiently. The results suggest that betaine could be a meaningful option for individuals who cannot exercise consistently due to mobility limitations or chronic conditions.
Does Betaine Help People Who Already Exercise
A key question is whether people who exercise regularly still benefit from betaine supplementation. Research shows that they do. The effects appear to be additive rather than redundant.
Real Performance Gains in Athletes
Several clinical studies demonstrate that trained individuals experience measurable improvements when supplementing with betaine:
• In a six week study, college athletes taking five grams of betaine daily gained strength in upper body, lower body, and overhead lifts.
• In another study, trained subjects taking two and a half grams of betaine daily performed more repetitions in squat exercises.
• CrossFit athletes taking betaine demonstrated better performance and increased testosterone levels.
Even in individuals who are already fit, betaine appears to provide an additional boost.
Why It Works: Three Major Mechanisms
More Fuel for Muscles
Betaine donates methyl groups that help the body make creatine, a key molecule used for quick energy during intense exercise. Although exercise raises natural betaine production, supplementation can push creatine production even higher.
Faster Recovery
Betaine helps protect muscle proteins, supports growth promoting hormones such as growth hormone and IGF 1, lowers cortisol after intense exercise, and improves the testosterone to cortisol ratio. Individuals taking betaine experience less muscle burn, recover faster, and perform more repetitions during training.
Better Cellular Protection
Betaine protects cells and mitochondria from stress. This may help the body adapt more effectively to exercise and reduce cellular damage from intense training.
The Better Together Effect
Studies show that combining exercise with betaine produces greater benefits than either one alone. Betaine appears to:
• Raise betaine levels higher than exercise alone
• Maintain elevated levels throughout the day
• Provide protection on rest days
• Support the body during other therapies such as NAD
For active individuals, this means enhanced performance, improved recovery, and better long term cellular health.
How Much Should You Take
Research supported doses include:
• Two grams daily for improved muscle endurance
• Three to five grams daily for strength and power
• Up to six grams daily in cardiovascular studies with good safety profiles
For general wellness, lower amounts may still be effective. I personally take fifteen hundred milligrams daily for five days each week.
The Betaine and NAD Connection
Betaine plays an important role in regenerative medicine, especially during intravenous NAD therapy. When the body processes NAD, it breaks it down into nicotinamide. The body then requires methyl donors, including betaine, to safely remove this substance.
If methyl donors are depleted, nicotinamide builds up, which can strain the liver and kidneys and cause side effects such as nausea or fatigue. Supplementing with betaine during NAD therapy prevents this problem and improves overall tolerance.
Heart Protection and Homocysteine Reduction
Betaine also reduces homocysteine, a harmful compound that can damage blood vessels and increase inflammation. By donating methyl groups, betaine converts homocysteine into a useful amino acid called methionine.
Clinical studies show that betaine can reduce homocysteine levels within hours, with maximum effects after four to six weeks. Lowering homocysteine has been linked to reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
This cardiovascular protection works together with betaine’s anti-inflammatory activity, creating a powerful dual benefit.
Clinical Application at PUR-FORM
At PUR-FORM we have used betaine for years as part of our IV NAD protocols. Our patients consistently report better tolerance, fewer side effects, and improved therapeutic results when using betaine.
The new research confirms what we have already observed. Betaine supports NAD metabolism, mimics many of the benefits of exercise, protects the heart and brain, and enhances training results in active individuals. It is rare to find a single compound with such broad and well supported effects across multiple systems.
What This Means for the Future
According to the study’s lead researcher, these findings help redefine the concept of exercise as medicine and highlight a new approach to longevity science. Betaine is safe, widely available, and effective at improving health across multiple organ systems.
For individuals who cannot engage in regular physical activity, betaine supplementation may offer access to many of the benefits of exercise. For active individuals, it can amplify results and extend long term healthspan.
Conclusion
Betaine is emerging as one of the most promising compounds in regenerative medicine and healthy aging. The kidneys naturally produce it during exercise, and it plays central roles in lowering inflammation, supporting NAD metabolism, protecting the heart, improving metabolism, and slowing cellular aging.
Whether used as part of IV NAD protocols, as a standalone anti aging intervention, or as a performance enhancer for athletes, betaine offers a unique combination of safety, versatility, and impact. It provides an option for those who cannot exercise and a powerful advantage for those who do.
– Dr. P
If you’d like to learn more, the original article is attached here.