In the pursuit of optimal health, recovery, and relief from various ailments, humans have increasingly turned to unconventional methods that harness the power of extreme temperatures. Two increasingly popular cold therapies, whole-body cryotherapy, and cold plunge pools, have gained traction among athletes, wellness enthusiasts, and those seeking relief. Here at PUR-FORM, we now offer both whole-body cryotherapy and contrast therapy. While both modalities involve exposing the body to frigid conditions, they differ in their approaches, potential mechanisms of action, and proposed benefits. Although cryotherapy chambers and cold plunge pools share the commonality of subjecting the body to freezing temperatures, they have distinct scientific differences that will be explored in greater detail, shedding light on the unique physiological responses associated with each approach.
What Is Whole-Body Cryotherapy?
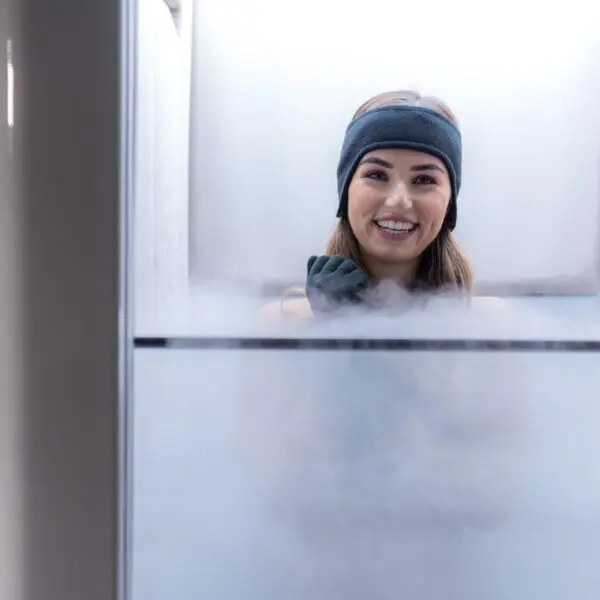
Whole-body cryotherapy involves an individual being exposed to extremely low temperatures, typically ranging from -180°F to -250°F for a brief period of 2 to 4 minutes. During a cryotherapy session, the person steps into a cryotherapy chamber or cryosauna, which envelops the body with nitrogen vapors. We are excited to announce our new cryotherapy machine is now up and running!
The Physiological Responses to Whole-Body Cryotherapy
When the body is exposed to the intense cold of whole-body cryotherapy, it elicits a series of physiological responses collectively known as the “cold shock response.” The sympathetic nervous system orchestrates this response and involves several key mechanisms:
Vasoconstriction: To preserve core body temperature, blood vessels in the skin and muscles constrict, reducing blood flow to the extremities while redirecting blood towards the core to maintain vital organ function.
Increased Metabolic Rate: The body works harder to generate heat and maintain its core temperature, increasing metabolic rate and calorie expenditure. A single cryotherapy session can burn 500-800 additional calories. The release of hormones such as norepinephrine and epinephrine facilitates this process.
Release of Endorphins and Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: Exposure to extreme cold triggers the release of endorphins, natural pain relievers, and mood elevators. Additionally, the body releases anti-inflammatory molecules, including interleukin-10 and adiponectin, which can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
Benefits of Whole-Body Cryotherapy
- Metabolic Boost and Potential Weight Management: Cryotherapy has been suggested to increase metabolism and calorie expenditure. Exposure to extreme cold may activate brown adipose tissue (BAT), a type of fat that generates heat and burns calories. While further research is needed, cryotherapy’s potential metabolic benefits have sparked interest in its role in weight management.
- Pain Relief: The release of endorphins and the reduction of inflammation can alleviate pain associated with conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and muscle soreness. A study published in the Journal of Thermal Biology found that cryotherapy significantly reduced pain and improved quality of life in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis.
- Improved Recovery: By reducing inflammation and promoting blood flow, cryotherapy may aid in faster recovery from injuries and intense physical activity. A systematic review published in the Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness suggested that cryotherapy could be an effective adjunct therapy for enhancing recovery and reducing muscle damage after exercise.
- Boosted Mood and Energy: The release of endorphins and the increased metabolic rate can lead to improved mood, increased energy levels, and better sleep quality. A study in the Journal of Affective Disorders found that cryotherapy sessions improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety in participants.
- Skin Rejuvenation: The constriction and dilation of blood vessels during cryotherapy may promote collagen production and improve skin texture. However, the evidence for this benefit still needs to be enhanced and requires further research.
What Are Cold Plunge Pools?
Cold plunge pools, also known as ice baths or cold water immersion, involve submerging the body in cold water, typically between 50°F and 60°F (10°C and 15°C), for a period ranging from 5 to 20 minutes, depending on individual tolerance. This practice has been utilized for centuries by athletes and wellness enthusiasts to promote recovery and overall health.
The Physiological Responses to Cold Plunge Pools
Like cryotherapy, cold plunge pools trigger the body’s cold shock response, leading to vasoconstriction, increased metabolic rate, and the release of endorphins and anti-inflammatory molecules. However, the mechanism of action differs slightly due to the direct contact with cold water, which can elicit additional physiological responses such as:
Hydrostatic Pressure: Water immersion creates hydrostatic pressure, which can aid in reducing swelling and inflammation by promoting lymphatic drainage and reducing edema (excess accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues).
Cardiovascular Adaptations: Alternating exposure to cold water and subsequent re-warming periods can improve cardiovascular function and circulation. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that regular cold water immersion enhanced endothelial function and nitric oxide production, essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels.
Benefits of Cold Plunge Pools
- Reduced Inflammation and Pain Relief: The release of anti-inflammatory molecules and endorphins during cold water immersion can help alleviate inflammation and pain associated with arthritis, muscle soreness, and injuries. A systematic review published in the Journal of Physiotherapy found that cold water immersion can effectively reduce delayed-onset muscle soreness and muscle fatigue after exercise.
- Improved Recovery: Cold plunge pools may aid in faster recovery from intense physical activity and exercise by reducing inflammation and promoting blood flow. A study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research demonstrated that cold water immersion after resistance training can enhance recovery and reduce muscle damage markers.
- Boosted Mood and Energy: The release of endorphins and the increased metabolic rate associated with cold water exposure can potentially lead to improved mood, increased energy levels, and better sleep quality. However, more research is needed to substantiate these claims, specifically for cold plunge pools.
- Cardiovascular Health: Similar to cryotherapy, alternating exposure to cold water and subsequent re-warming periods can improve cardiovascular function and circulation, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Skin Rejuvenation and Toning: Cold water exposure has a toning effect on the skin. It constricts the pores, reducing the accumulation of dirt and sebum and leaving the skin refreshed and tightened. Cold plunge pools may also stimulate collagen production, improving skin tone and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. The cold water invigorates the skin, promoting a healthy and radiant complexion.
Distinct Differences Between Whole-Body Cryotherapy and Cold Plunge Pools
- Temperature Extremes: Cryotherapy exposes the body to extremely low temperatures ranging from -200°F to -250°F, while cold plunge pools typically maintain water temperatures between 40°F and 60°F, which is less extreme than cryotherapy but still significantly below average body temperature.
- Duration of Exposure: Cryotherapy sessions are generally short-lived, lasting between 2 and 4 minutes, whereas cold plunge pool sessions can extend from 5 to 10 minutes, depending on individual tolerance and the specific protocol employed.
- Method of Cold Exposure: In cryotherapy, the body is exposed to cold nitrogen vapors, while cold plunge pools involve direct immersion in cold water, which can create additional physiological effects due to the hydrostatic pressure exerted on the body.
- Accessibility and Cost: Cold plunge pools are generally more accessible and less expensive than cryotherapy chambers, which require specialized equipment and trained personnel to operate safely and effectively.
Scientific Review of Whole-Body Cryotherapy
A systematic review published in the Journal of Thermal Biology found that cryotherapy can reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage. However, the authors cautioned that the quality of the evidence was low to moderate. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness demonstrated that cryotherapy could improve muscle recovery and reduce muscle damage markers after intense exercise. However, the effects were modest and short-lived.
Scientific Review of Cold Plunge Pools
Research from the Journal of Physiotherapy shows cold water immersion can reduce delayed-onset muscle soreness and fatigue after exercise, though the optimal temperature and duration are still unclear. A study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found it enhances recovery and reduces muscle damage markers, primarily within 24 hours post-exercise. Additionally the International Journal of Sports Medicine suggests potential cardiovascular benefits from cold water immersion.
Choosing the Right Chill for You
- Immersion and Full-Body Experience: if you enjoy the tactile sensation of water and crave a complete body submersion, cold plunge pools may be your ideal choice. They offer a refreshing and invigorating experience that can energize both mind and body.
- Intense Cold Exposure: If you prefer a shorter and more intense cold exposure experience, whole-body cryotherapy may be more suitable for you. It provides a quick blast of frigid air to invigorate your senses and deliver wellness benefits.
- Individual Comfort and Accessibility: Consider your comfort level with each method and the availability of facilities. Some individuals may find the idea of submerging in cold water more appealing and accessible, while others may prefer the controlled environment of cryotherapy.
While both whole-body cryotherapy and cold plunge pools show promise as potential therapeutic modalities, It’s important to note that the scientific evidence supporting the benefits of cold plunge pools and whole-body cryotherapy is still evolving, and individual responses may vary. As with any therapy, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals and understand potential risks or contraindications.
– Dr. Purita
You may also enjoy reading: