Many of our patients know I am a strong supporter of molecular hydrogen. A new scientific paper adds an important piece to the puzzle and helps explain why hydrogen has such wide-ranging benefits. For those of us working in regenerative medicine, this is meaningful because it connects hydrogen directly to mitochondrial signaling and cellular repair.
Most people think of hydrogen as a simple antioxidant. Recent research shows something far more interesting: hydrogen acts as a gentle training signal for your mitochondria, the energy centers of every cell. Instead of simply neutralizing free radicals, hydrogen temporarily slows part of the mitochondrial engine. This slowdown triggers the cell to strengthen and repair itself.
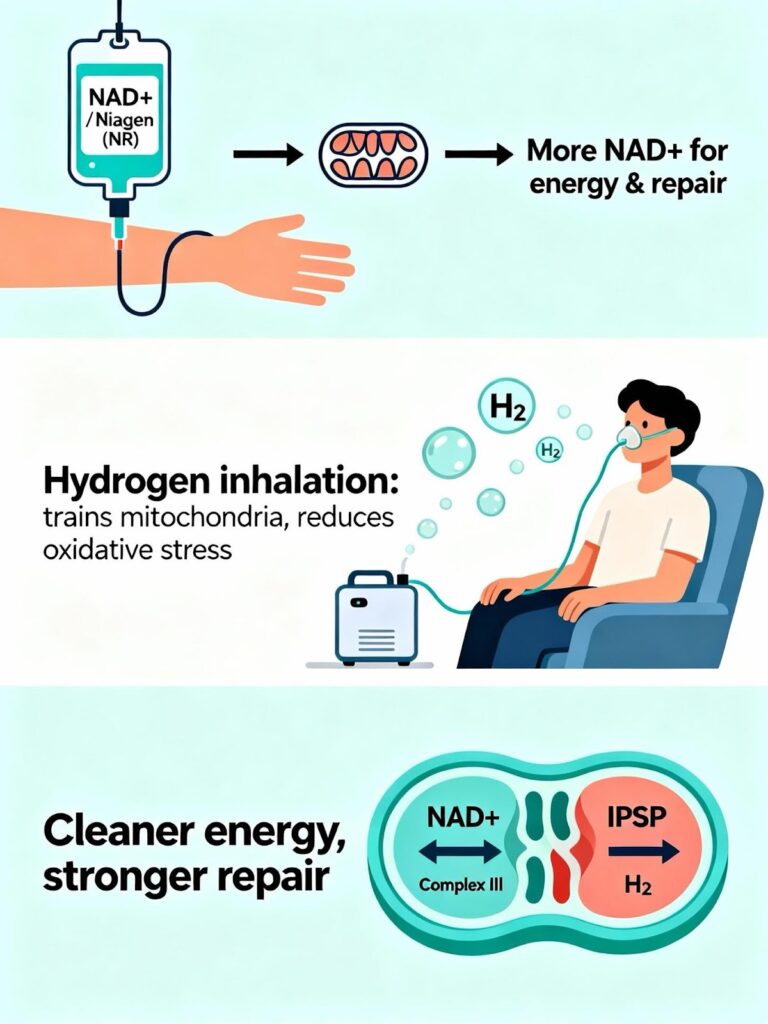
How Hydrogen Sends a Training Signal to Your Cells
Hydrogen interacts with a section of the mitochondrial machinery called complex III. More specifically, it targets a component known as the Rieske iron–sulfur protein (RISP). This temporarily reduces mitochondrial activity, which creates a short dip in:
- ATP production
- Mitochondrial membrane potential
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
To the cell, this appears as mild stress. It is similar to what happens during exercise or fasting.
In response, the cell activates an important protective system called the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt). Think of this as the mitochondria’s internal repair mode. It increases the production of protective proteins, improves quality control, and stimulates the creation of new mitochondrial components.
A few hours later, something remarkable happens. The mitochondria recover stronger than before. Energy production increases, membrane potential improves, and ROS signaling becomes more controlled and efficient. In simple terms, hydrogen conditions mitochondria to perform at a higher level.
Why This Matters for Healing and Longevity
Most regenerative therapies, including PRP, stem cells, peptides, and photobiomodulation, depend on healthy and adaptable mitochondria. These tiny structures determine how well your cells repair, how easily they handle inflammation, and whether they survive after injury.
Hydrogen supports this process through a mechanism known as mitohormesis. This describes a small and controlled stress that leads to a larger beneficial adaptive response. Because hydrogen is extremely safe, non-toxic, and easy to deliver through inhalation or hydrogen-rich water, it can be added to regenerative programs to:
- Protect tissues from oxidative stress
- Improve mitochondrial recovery
- Enhance cell survival
- Strengthen long-term repair capacity
Hydrogen should not be viewed as a regular antioxidant. It works as a precise mitochondrial modulator that helps the body repair more effectively while allowing healthy cellular signals to remain intact.
Hydrogen and NAD: Why They Work Better Together
The clinical relevance of hydrogen becomes even clearer when we look at how it interacts with intravenous NAD-based therapies.
NAD⁺ is a central molecule that mitochondria use to make energy and activate enzymes involved in repair, inflammation control, and stress resistance. IV NAD⁺ raises levels rapidly. This rapid rise can sometimes feel overwhelming for patients, especially if the infusion rate is fast. Symptoms may include:
- Head pressure
- Chest tightness
- Nausea
- Flushing
- Anxiety or restlessness
These effects usually reflect a sudden increase in metabolic activity.
Hydrogen can help smooth this experience. By gently modulating electron flow at complex III and activating UPRmt, hydrogen helps mitochondria run cleanly with fewer oxidative byproducts and less inflammatory flare. When NAD⁺ increases mitochondrial workload, hydrogen-conditioned mitochondria are better prepared to manage that increased demand.
In practical terms, this may lead to:
- Fewer uncomfortable symptoms during NAD infusions
- More efficient use of the NAD⁺ delivered
- Better activation of repair pathways
- A calmer and more stable physiologic response
Formal clinical trials on the combination have not yet been completed. However, the mechanistic fit is compelling. NAD⁺ provides the biochemical fuel, while hydrogen strengthens the mitochondrial hardware.
Why Niagen May Be Even Smoother
PurForm recently introduced IV Niagen, also known as nicotinamide riboside (NR). Niagen is a precursor to NAD⁺. Instead of infusing NAD⁺ directly into the bloodstream, we deliver NR, and cells convert it into NAD⁺ internally.
Many patients tolerate this approach more easily because it supports the cell’s natural NAD-producing machinery instead of flooding the bloodstream with high levels of free NAD⁺.
Preclinical research shows that Niagen:
- Boosts mitochondrial NAD⁺
- Activates mitochondrial sirtuins
- Improves energy production
- Reduces oxidative stress
Pairing Niagen with hydrogen creates a similar synergy:
- Niagen builds the NAD⁺ pool from within
- Hydrogen optimizes mitochondrial electron flow and reduces stress
This combination may offer a smoother and more effective upgrade in mitochondrial health.
Ultimately, both NAD⁺ and Niagen raise NAD levels effectively. The better choice depends on your time constraints, sensitivities, and budget.
Putting It All Together for Better Cellular Health
Hydrogen is more than an antioxidant. It is a conditioning tool for mitochondria, and healthier mitochondria create healthier cells. When combined with NAD⁺ or Niagen, it prepares the body to repair more efficiently and with less discomfort.
These same principles can extend to regenerative procedures such as PRP series, stem cell injections, or high-intensity photobiomodulation. The goal is not simply to increase inputs. The goal is to help your cells respond more intelligently, repair more thoroughly, and stay resilient over time.
Hydrogen adds to this in a meaningful way.
— Dr. P