BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS THAT OCCUR IN LIVING CELLS IN RESPONSE TO LIGHT THERAPY
The chamber uses the principles of Photo Bio Modulation to enhance, stimulate, and activate stem cells, platelets, Red Blood Cells, Leukocytes, Fibroblasts, fat grafts and other cells found in autologous biologics. It can help increase the efficiency of essentially any autogenous biologic. The PBM chamber is an interventional medical therapy providing physical stimulus on a biologic typically found in either a ten or twenty CC syringe. It gives the physician the ability to induce biological changes inside, or outside of cells, by using the radiation and the scattering properties inherent in light of differing wave lengths. This is accomplished by the propagating light stream interacting with the aggregate tissue target resonating at the same wave length front. This has been and will continue to be a Regenerative Medicine game changer.
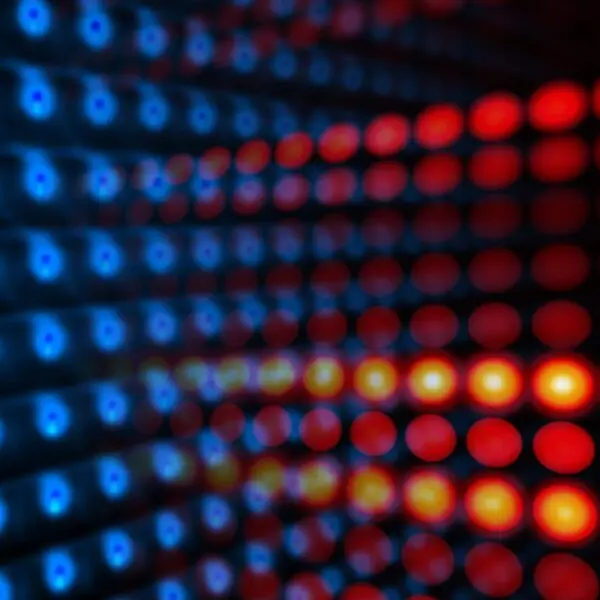
The following is a picture of the inner chamber in action:

It is a picture of the interior showing Red and Green LED light strips, mirrors etc. The syringe is placed into opening and subjected to the various light wavelengths.
The Photonic Chamber excites photo receptors within the cell body or the cell surface. It can accomplish this on an atomic or molecular basis affecting the molecules which compose living tissue. It will create a dependent sensory and biochemical alteration in the radiated tissues. It is recommended that all autologous biologics should be subjected to PBM for 10-20 minutes before injection to realize maximum benefit. Typically, the exposure time is 10 minutes for a PRP product and 20 minutes for a nucleated cell product such as bone marrow aspirate, fat graft, SVF, and Very Small Embryonic Like Stem Cells etc.
The following photograph shows the chamber with both a 10 CC and 20 CC syringe undergoing Photo Bio Modulation:

The chamber has primary Red and Green colors but will also have Blue, Orange, and Yellow spectrums adding additional benefits.
A SUMMATION OF THE MECHANISM OF PBM CHAMBER THERAPY
The precise biochemical mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of photo modulation are not well known but the effects are found to be quite beneficial on multiple levels. One of the most distinctive features of LED light therapy relative to other modalities is that the effects are mediated not through induction of thermal effects but rather through a photobiostimulation.
At the most basic level, light therapy acts by inducing a photochemical reaction in the cell, a process referred to as bio stimulation or Photobiomodulation. This process involves intracellular photoreceptors. The photons must be absorbed by electronic absorption bands belonging to some molecular chromophores or photoreceptors. A chromophore or photoreceptor is a molecule (or part of a molecule) where the energy difference between electrons in two different molecular orbitals falls within the energy possessed by photons in the visible spectrum. What we do know is that it appears that photo modulation therapy has a wide range of effects at the molecular, cellular, and tissue levels. There are several pieces of evidence that point to a chromophore within mitochondria being one of the initial targets of light therapy. Within the cell, there is strong evidence to suggest that Red light therapy acts on the mitochondria to increase adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the induction of transcription factors. A transcription factor (TF), also called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor, is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA by binding to a specific DNA sequence. These transcription factors have significant importance in Regenerative Medicine. The transcription factors are regulated by changes in cellular redox state. Some of these redox factors include nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), p53, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1, and HIF-like factor. These transcription factors then cause protein synthesis that triggers further effects down-stream. These effects include increased cell proliferation and migration, modulation in the levels of cytokines, growth factors and inflammatory mediators, and increased tissue oxygenation.
There are three major intracellular photoreceptors. These include Cytochrome c Oxidase, Porphyrins, and Flavoproteins. Flavoproteins are group of protein complexes containing a riboflavin group. Flavoproteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, and DNA repair. Realize that NADH which is involved in the NAD/NADH cycle ATP production is a flavoprotein. There are also a number of other compounds that also act as photoreceptors such as Vitamins B6 and K. There are other compounds that are photo sensitive but that id for another discussion.
Evidence indicates that cytochrome c oxidase (CCO), also known as complex 4, is a very crucial chromophore in the cellular response to light therapy. It is most stimulated around 650Nm wavelength (red light). CCO is a component of the respiratory electron transport chain. The precise manner in which light affects CCO is not yet known. The observation that Nitric Oxide (NO) is released from cells during light therapy has led to speculation that CCO and NO release are linked by two possible pathways. It is possible that light therapy may cause photodissociation of NO from CCO. Nitric Oxide is an extremely important signaling molecule preforming multiple tasks.
The influence of light therapy on the electron transport chain extends far beyond simply increasing the levels of ATP produced by a cell. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and is, in the process, converted to water. Part of the oxygen that is metabolized produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a natural by-product. ROS are chemically active molecules that play an important role in cell signaling, regulation of cell cycle progression, enzyme activation, and nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Because PBM promotes the metabolism of oxygen, it also acts to increase ROS production (remember that mild oxidative stress is beneficial). In turn, ROS activates transcription factors, which leads to the upregulation of various stimulatory and protective genes. These genes are most likely related to cellular proliferation, migration, and the production of cytokines and growth factors, which have all been shown to be stimulated by light therapy.
Immune cells, in particular, appear to be strongly affected by Photo Modulation. Mast cells, which play a crucial role in the movement of leukocytes, are of considerable importance in inflammation. Specific wavelengths of light are able to trigger mast cell degranulation, which results in the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-a from the cells. This leads to increased infiltration of the tissues by leukocytes. However, in the long run this will help stimulate anti-inflammatory pathways. Photo modulation also enhances the proliferation, maturation, and motility of fibroblasts, and increases the production of basic fibroblast growth factor. Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) that signal through FGF receptors (FGFRs) regulate a broad spectrum of biological functions, including cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. Lymphocytes become activated and proliferate more rapidly, and epithelial cells become more motile, allowing wound sites to close more quickly. The ability of macrophages to act as phagocytes is also enhanced under the application of light therapy. Remember, that phagocytosis of MSCs will result in the production of T-reg cells which have a long-term effect on tissue repair and decreased auto found in the autologous biologics that are injected.
SPECIFIC ACTIONS OF THE VARIOUS WAVELENGTHS

The above illustration shows the various wavelengths (Red, Blue, and Green) and their actions on the cells.
The above diagram is an excellent illustration of the aspects of the Photonic Chamber as related to various wavelengths of light. We must realize that the Optical chamber does have two main colors, Red and Green, yet realize that there is a bleeding of colors. For instance, the Red Led light also has some Orange and Yellow that will “bleed out”. Thus, we are getting wavelengths of mainly Red in the vicinity of about 650 Nano meters but at the same time getting some wavelengths of Orange and even a bit of Yellow. The Green Led strip has a wavelength of 540Nm and it bleeds into the Blue and Yellow spectrum. One interesting bit of information is that chemicals appear a particular color to our eyes based on the wavelengths of light they reflect. Hemoglobin bound to oxygen absorbs blue-green light, which means that it reflects red-orange light into our eyes thus appearing red. That’s why blood turns bright cherry red when oxygen binds to its iron.
Let us talk about the specific colors. The Red LED and the bleeding of Yellow and Orange from the Red LED. One of the most general benefits of light therapy in these wavelengths is the production of ATP. Perhaps the most well-known aspects of the Red light concern its effects on the mitochondria of cells. It has been observed that mitochondria are changed to so called “giant mitochondria” after irradiation resulting in activation of various metabolic pathways and increased production of ATP. As stated earlier, ATP production comes from the actual stimulation of the Cytochrome C Oxidase. ATP production is observed in all cells. BECAUSE THERE IS MORE ATP PRODUCTION BY THE EFFECTS OF RED LIGHT, THE SECONDARY EFFECT IS TO PROMOTING STEM CELL DIFFERENTIATION. This occurs due to shifting the metabolic profile from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation due to the increased mitochondrial number and activity induced by the light exposure. It is known that this metabolic switch, glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation, is a key factor in stem cell differentiation. Remember when these biologics are injected into the joint ATP may be at a premium given the harsh conditions of the joint.
Although lacking nucleus, platelets also contain functional mitochondria thus subjected to PBM. On PBM activation, platelets produce extracellular vesicles known as microparticles. Platelet microparticles are very similar to exosomes except they appear to be more plentiful. The microparticles contain little snippets of RNA which give direction to cells. It is hypothesized that activated platelets also release their mitochondria with the microparticles. Both the mitochondria and microparticles can have significant effects on various cells. Photo Bio Modulation also increases the generation of platelets from precursor cells called megakaryocytes (MKs). It appears that Red light is instrumental in in helping to release the platelet micro particles. Red light energy irradiation helps bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration and proliferation, inhibits bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis, which contributes to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration to targeted tissue.
Another important aspect of PBM is pronounced anti-inflammatory effects. While the exact cellular signaling pathways responsible for this anti-inflammatory action are not yet completely understood, it is becoming clear that both local and systemic mechanisms are operating. Reductions in markers of oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines are well established after PBM. It has been noted by some studies that after photo bio modulation there has been increases in Interleukin-10 and Interleukin-1 antagonist. These increases will dramatically affect the clinical outcomes by reducing pain, inflammation and swelling.
It appears that both Red and especially Green light will be helpful in the polarization of Macrophages M-1 and M-2 types. The light therapy will increase polarization of the Macrophages to the M-2 type which are instrumental in tissue healing. M-1 macrophages are more important in dealing with bacterial infections. The M-2 macrophages help in the production of collagen formation.
Several parameters showed that green light was even more potent to stimulate proliferation and migration of endothelial cells than clinically well-established red-light therapy. Other effects attributed to the green light include decreases in lactic acid, reduced blood viscosity and improved oxygen affinity by the effects green light has on the hemoglobin molecule. Green light seems to stimulate the Flavoproteins which mediate a wide array of biological processes such as quenching of oxidative stress-induced radicals, DNA repair, and apoptosis.
When the Green color bleeds into the Blue light spectrum range there are some studies which hint that Blue light may have a therapeutic effect on exosomes. It can be beneficial in the release of exosomes from cells.
THE SUMMATION THE EFFECTS OF PHOTONICS CHAMBER ON REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
- DIRECT EFFECT ON THE VIABILITY OF STEM CELLS BY INCREASING MITOCHONDRIAL EFFICIENCY AND SIZE ULTIMATELY PRODUCING MORE ATP AND GREATER CELL SURVIVAL.
- HELPING IN THE STABILIZATION OF STEM CELL AND OTHER CELL MEMBRANES.
- DIRECT EFFECT ON THE LEUKOCYTES ULTIMATELY PRODUCING INCREASED AMOUNTS ON IL-10 AND IL-1 A MAKING FOR AN ANTI-INFLAMMATORY NICHE. THE PRACTICAL CLINICAL RESULT IS THAT TYPICALLY THE PATIENT HAS MUCH LESS POST INJECTION PAIN.
- DIRECT EFFECT ON MACROPHAGE POLORIZATION DIRECTING THE POLORIZATION TO M-2 MACROPHAGES WHICH CONTRIBUTE TO TISSUE REGENERATION.
- POSSIBLE INCREASED PRODUCTION AND RELEASE OF EXOSOMES INCLUDING INCREASED RELEASE OF PLATELET MICROPARTICLES.
- NITRIC OXIDE IS RELEASED BY THE CELLS AND MAY HAVE A BENEFIT ON THE CELLUAR ENVIRONMENT.
- FORMATION OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS WHICH HAVE IMPLICATIONS ON MULTIPLE LEVELS DOWNSTREAM.
- ENHANCES BONE MARROW MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL MIGRATION AND PROLIFERATION, INHIBITS BONE MARROW MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL APOPTOSIS
- SUPPRESSES INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE OF HUMAN ADIPOSE-DERIVED STEM CELLS BY MODULATING INTRACELLULAR CYCLIC AMP LEVEL AND NF-ΚB ACTIVITY
- BY INCREASEING THE AMOUNT OF ATP AVAILABLE, A METABOLIC SWITCH (GLYCOLYSIS TO OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION) IS TURNED ON WHICH IS A KEY FACTOR INDUCING STEM CELL DIFFERENTIATION.
The chamber will make a significant difference in the success one will have using a variety of autologous cell products. Pain, swelling and inflammation will be diminished. Across the board the cells will typically be healthier and have a better chance of longevity in their perilous journey in the joint, tendon, or other area into which they are injected. I have used the Photo Bio Modulation techniques for many years. We have now made the technology available to numerous Regenerative Medicine doctors at a very reasonable price.